背景
アカツキではRailsでゲームサーバを開発しています。インフラはAWSにあり、CloudFormation, Chef, Capistrano を用いて、Infrastructure as Code を実現しています。
エンジニアは普段ローカルマシンで開発していますが、ディレクター、レベルデザイナーなどは定義ファイルを変えた後、それを反映して動作を確認するための検証サーバ(以下、検証環境)を使っています。
検証環境へのデプロイも Capistrano で自動化しており、最初は問題が無かったのですが、ゲーム上のデータが増えることによって、一度のデプロイで10分程度かかるようになっていました。
以下、Capistrano ver.2系の話にはなりますが、検証環境のデプロイを高速化したので、その内容を紹介したいと思います。
現状分析
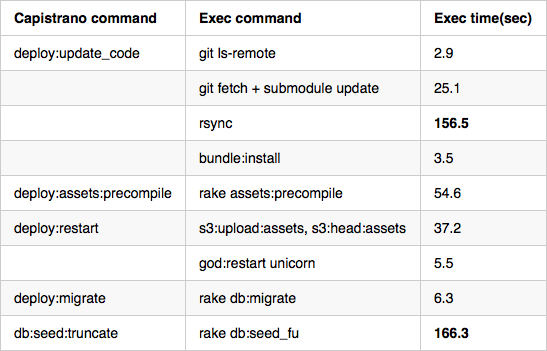
rsync について、capistrano_rsync_with_remote_cache を利用して高速化していますが、リポジトリ容量が約6GBあり、以下ログの通り cached-copy ディレクトリからの cp (rsync) にも時間がかかるようになっていました。
#!ruby
* executing `deploy:update_code'
executing locally: "git ls-remote git@github.com:aktsk/repository.git develop"
command finished in 3011ms
executing locally: cd /Users/jenkins/.jenkins/jobs/repository-deploy-dev/workspace/.rsync_cache && git fetch -q origin && git fetch --tags -q origin && git reset -q --hard commit_hash && git submodule -q init && git submodule -q sync && export GIT_RECURSIVE=$([ ! "`git --version`" \< "git version 1.6.5" ] && echo --recursive) && git submodule -q update --init $GIT_RECURSIVE && git clean -q -d -x -f
command finished in 25081ms
executing locally: rsync -az --delete --delete-excluded --exclude=Capfile --exclude=Guardfile --exclude=cache --rsh='ssh -p 22' /Users/jenkins/.jenkins/jobs/repository-deploy-dev/workspace/.rsync_cache/ deployer@host:deploy_path/development/shared/cached-copy/
command finished in 5781ms
* executing "rsync -a --delete deploy_path/development/shared/cached-copy/ deploy_path/development/releases/version/"
servers: ["host"]
[host] executing command
command finished in 122275ms
また、db:seed:truncate は、DB上のデータをクリアして rake db:seed_fu( seed-fu ) を実行する処理ですが、毎回全てをロードしているため、これもデプロイが遅い要因となっています。
対応策
rsync については、Gitのリポジトリを毎回コピーするのではなく、レポジトリを一つにしてタグによる差分管理を行えば速くなりそうです。
以下、CodeClimate社や、Github社で行っているやり方が参考になります。
- http://blog.codeclimate.com/blog/2013/10/02/high-speed-rails-deploys-with-git/
- https://github.com/blog/470-deployment-script-spring-cleaning
同じ様なことを実現する方法として、Recap というGemを導入する方法もありますが、デフォルトのコマンドを置き換えてしまうこと、Ubuntu のサポートに限定していること、そう難しい仕組みでもないことから、名前空間を分けて新しく作ることにしました。
また、毎回実行していた db:seed:truncate や、deploy:assets:precompile などは、更新があった時だけ実行すれば良さそうです。
どのように対応したか
Capistrano拡張
全体のコードを以下に公開しています。ユーティリティやリリース管理はRecapのソースほぼそのままです。
https://gist.github.com/yusuket/11398285
個別の解説を以下に記載します。
コマンドユーティリティ
今回追加する処理で利用される git, bundle コマンド等のユーティリティメソッドを事前に定義しておきます。
# Run a git command in the `current_path` directory
def git(command)
run "cd #{current_path} && umask 002 && git #{command}"
end
# Capture the result of a git command run within the `current_path` directory
def capture_git(command)
capture "cd #{current_path} && umask 002 && git #{command}"
end
def exit_code(command)
capture("#{command} > /dev/null 2>&1; echo $?").strip
end
def run_current(command)
run "cd #{current_path} && RAILS_ENV=#{rails_env} #{command}"
end
def run_bundle(command)
run_current "bundle exec #{command}"
end
リリース管理
rails_env の値 + 実行時刻をリリース管理用のタグ名としており、リリース履歴を git tag | grep ^rails_env によって一覧化出来るようにしています。 また、実行時刻をタグ名にすることにより、 git tag でリリース順に出力される様になるので、直前のリリースタグ を .last で取得出来るようになります。
直前のリリースからどのファイルに変更があったか?についても、git diff を使って確認でき、Gitの速さの恩恵を得ることが出来ます。 更に changed_files メソッドではその結果をインスタンス変数にキャッシュしており、何度差分確認をしても安定した実行速度となります。
def release_tag_from_repository
rails_env + '/' + Time.now.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
end
# Find the latest tag from the repository. As `git tag` returns tags in order, and our release
# tags are timestamps, the latest tag will always be the last in the list.
def latest_tag(use_cache=true)
return @latest_tag if use_cache && @latest_tag
tags = capture_git("tag").strip.split
@latest_tag = tags.grep(/\A#{rails_env}\/[0-9]{14}\Z/).last
end
# Does the given file exist within the deployment directory?
def deployed_file_exists?(path, root_path = current_path)
exit_code("cd #{root_path} && [ -f #{path} ]") == "0"
end
# Has the given path been created or changed since the previous deployment? During the first
# successful deployment this will always return true if the file exists.
def deployed_file_changed?(path)
return deployed_file_exists?(path) unless latest_tag
exit_code("cd #{current_path} && git diff --exit-code #{latest_tag} origin/#{branch} #{path}") == "1"
end
def changed_files
@changed_files ||=
if latest_tag
capture_git("diff --name-only #{latest_tag} origin/#{branch} | cat").split
else
capture_git("ls-files | cat").split
end
end
def trigger_update?(path)
changed_files.detect {|p| p[0, path.length] == path}
end
おまけ
以下は今回の高速化について関係の無いメソッドなので、読み飛ばして頂いてかまいません。
おまけ:AWSタグ関連
アカツキではインフラ環境を全てAWSで統一しており、役割の違うEC2インスタンスが複数起動しています。構成が変わる度にどのサーバにデプロイするかをいちいち設定していては面倒なので、AWSのRoleタグによってデプロイ先を判断しています。
例えば、deploy.rbに、set :tag_key, 'Role', deploy/config/[environment].rb に tag 'prod-web', :web と記載します。これは、Role タグに prod-web が設定されている起動中のインスタンスを対象に、Capistrano上の :web というロールを設定する、という意味になります。
def tagged_servers(tag_key, tag_value, default=[])
@ec2 ||= AWS::EC2.new(ec2_endpoint: 'ec2.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com')
ret = @ec2.instances.map do |instance|
next if instance.tags[tag_key] != tag_value
next if instance.status != :running
instance.dns_name || instance.ip_address || instance.private_dns_name
end.compact
return default if ret.empty?
ret
end
def tag(tag_value, *args)
AWS.memoize {
tagged_servers(tag_key, tag_value).each do |host|
server(host, *args)
end
}
end
def first_server(tag_value)
AWS.memoize {
tagged_servers(tag_key, tag_value).first
}
end
おまけ:GOD
Unicornのプロセス管理は GOD によって行っていますので、そのコマンドユーティリティを定義しています。
def god_execute(act, name)
"cd #{current_path} && #{god_cmd} #{act} #{name}"
end
def god_status_cmd(name='')
"cd #{current_path} && #{god_cmd} status #{name} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null"
end
def god_config_reload(config_name)
"cd #{current_path} && #{god_cmd} load config/god/#{config_name}.god"
end
def start_process(proc, conf, act)
script = <<-END
set -x;
if #{god_status_cmd(proc)}; then
#{act == :restart ? god_execute(:restart, proc) : "echo running"};
else
#{god_config_reload(conf)};
#{god_execute(:start, proc)};
fi
END
run script
end
おまけ:Template
デプロイ先の設定ファイルは template ディレクトリで管理しています。以下 conf_template メソッドは、設定ファイル上の変数を実行時のコンテキストで置き換えた結果を返します。
def conf_template(file, binding)
dir = File.join(File.dirname(__FILE__), '..', 'templates')
Erubis::Eruby.new(File.read("#{dir}/#{file}.erb")).result(binding)
end
config/deploy.rb
https://gist.github.com/yusuket/11399283
これも個別に解説していきます。
名前空間
名前空間を、deploy:simple に定義しています。
namespace :deploy do
namespace :simple do
Setup
あらかじめディレクトリをつくり、git cloneしておきます。
レポジトリは #{deploy_to}/releases/current ディレクトリに配置し、current_pathからはそこへのシンボリックリンクを貼ることとしました。 また、Nginxのserver設定を変更したくなかったので、shared_path も既存の通りに構成することとしました。
desc "Setup a GitHub-style deployment."
task :setup, :except => { :no_release => true } do
transaction do
on_rollback { run "rm -fr #{deploy_to}" }
run "mkdir -p #{releases_path}"
run "chmod g+rw #{releases_path}"
# Then clone the code and change to the given branch
git "clone #{repository} #{releases_path}/current"
git "reset --hard origin/#{branch}"
run 'git config --global user.email "<deploy-user-email>"'
run 'git config --global user.name "<deploy-user-name>"'
end
end
after "deploy:simple:setup", "god:start"
namespace :symlinks do
desc "Make all the symlinks"
task :make, :roles => :app, :except => { :no_release => true } do
symlinks = {
'assets' => 'public/assets',
'system' => 'public/system',
'log' => 'log',
'pids' => 'tmp/pids',
'sockets' => 'tmp/sockets',
}
# needed for some of the symlinks
run "rm -rf #{current_path} && ln -s #{releases_path}/current #{current_path}"
run "mkdir -p #{releases_path}/current/tmp"
commands = symlinks.map do |from, to|
"rm -rf #{current_path}/#{to} && mkdir -p #{shared_path}/#{from} && ln -s #{shared_path}/#{from} #{current_path}/#{to}"
end
commands << "rm -rf #{shared_path}/log && ln -s /media/ephemeral0/rails #{shared_path}/log"
run "cd #{current_path} && #{commands.join(" && ")}"
end
after "deploy:simple:setup", "deploy:simple:symlinks:make"
end
コードの更新は、git fetch と git reset --hard で 行います。
desc "Update the deployed code."
task :update_code, :except => { :no_release => true } do
on_rollback { git "reset --hard #{latest_tag}" if latest_tag }
git "fetch && git reset --hard origin/#{branch}"
run_current "bundle install" if trigger_update?("Gemfile.lock")
end
after "deploy:simple:setup", "deploy:simple:update_code"
リリースバージョンは、タグにより管理します。 デプロイが完了した時点で以下のタスクを実行する様に、Jenkinsのジョブを設定しています。
# Tag `HEAD` with the release tag and message
desc "Update the REVISION."
task :tag, :except => { :no_release => true } do
set :release_tag, release_tag_from_repository
set :release_message, "Deployed at #{Time.now}"
on_rollback { git "tag -d #{release_tag}" }
if changed_files.count > 0
git "tag #{release_tag} -m '#{release_message}'"
end
end
rails_root/template 以下に各種設定ファイルを配置しています。更新があれば、デプロイ先にコピーされるようにしています。
set(:setup_database_triggers, %w(templates/database.yml.erb templates/shards.yml.erb))
namespace :conf do
desc 'Setup database.yml on simple deploy'
task :database do
if setup_database_triggers.detect {|path| trigger_update?(path)}
put conf_template('database.yml', binding), "#{current_path}/config/database.yml"
unless slaves.empty?
put conf_template('shards.yml', binding), "#{current_path}/config/shards.yml"
end
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:conf:database"
desc 'Setup memcached.yml'
task :memcached do
if trigger_update?('templates/memcached.yml.erb')
put conf_template('memcached.yml', binding), "#{current_path}/config/memcached.yml"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:conf:memcached"
desc 'Setup redis.yml'
task :redis do
if trigger_update?('templates/redis.yml.erb')
put conf_template('redis.yml', binding), "#{current_path}/config/redis.yml"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:conf:redis"
end
desc "Create database"
task :create_database, :roles => :db, :except => { no_release: true } do
if setup_database_triggers.detect {|path| trigger_update?(path)}
run "cd #{current_path} && bundle exec rake db:create"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:conf:database", "deploy:simple:create_database"
rake db:create, rake db:migrare や rake assets:precompile も、更新があった場合のみ実行するようにしています
ジョブ実行時間が長い原因だった rake db:seed_fu も、対象のファイルが更新されている場合だけ、そのファイルのみロードするように変更しました。
desc "Create database"
task :create_database, :roles => :db, :except => { no_release: true } do
if setup_database_triggers.detect {|path| trigger_update?(path)}
run "cd #{current_path} && bundle exec rake db:create"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:conf:database", "deploy:simple:create_database"
desc 'Run the migrate rake task if migrations changed.'
task :migrate do
if trigger_update?('db/migrate')
run_bundle "rake db:migrate"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:migrate"
namespace :seed do
[:update, :truncate].each do |act|
desc "#{act} Game Master data if changed from previous version."
task act, :roles => :db, :except => {no_release: true} do
cond = act == :truncate ? "TRUNCATE=1" : ""
if trigger_update?("db/seeds")
tables = changed_files.grep(/\Adb\/seeds.*\.yml\Z/).map{|p| p.split('/').last.gsub('.yml', '') }
run_bundle "rake db:seed_fu TABLES=#{tables.join(',')} #{cond}"
end
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:seed:update"
end
namespace :assets do
set(:asset_precompilation_triggers, %w(app/assets vendor/assets Gemfile.lock config))
desc 'Run the asset precompilation rake task if assets changed.'
task :precompile do
if asset_precompilation_triggers.detect {|path| trigger_update?(path)}
run_bundle "rake RAILS_GROUPS=assets assets:precompile"
end
end
after "deploy:simple:update_code", "deploy:simple:assets:precompile"
end
ロールバックは、直前のリリースタグに向けて、reset --hard します。
desc "Rollback to previous release."
task :rollback, :except => { :no_release => true } do
if latest_tag
git "tag -d #{latest_tag}"
git "reset --hard #{latest_tag(false)}"
restart
else
abort "This app is not currently deployed"
end
end
Capfile
拡張コードはデプロイタスクの前にロードするよう、Capfileで指定しました。
load 'deploy'
load 'deploy/assets' # Uncomment if you are using Rails' asset pipeline
load 'config/deploy/capistrano_extention'
load 'config/deploy' # remove this line to skip loading any of the default tasks
結果
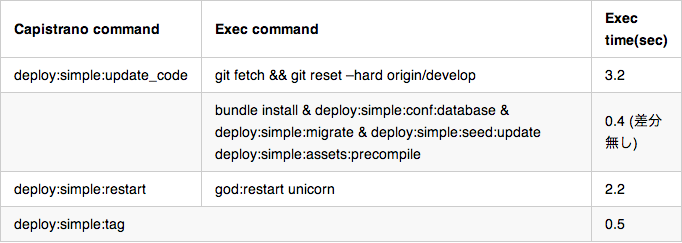
Jenkinsで実行している git fetch + bundle install と合わせ、ジョブ実行時間が 約19秒 になりました。
capistrano コマンドの実行速度だけを見ると、約6秒 で終わっています。
ただし、これはアプリケーションコードの差分だけがあり、データの更新差分が無かった場合です。全てのデータが更新されていれば7分強の実行時間になるはずですが、実運用でそのようなことは稀で、8割のジョブはは1分以内、長くても4分程度の実行時間となりました。
まとめ
一回のデプロイ時間は最大9分程度の改善ですが、検証環境のデプロイは、1日に20~30回実行されています。
一日の改善は3時間程度であり、一ヶ月で3.75日程度、一年で一ヶ月半分の時間的コストを改善していると言えます。
Git tag 方式でのリリース管理の懸念点として、Git管理していないファイルを含めた rollback が出来ないということがありますが、検証環境ではまず問題になることは無いでしょう。
定期的に普段の業務タスクのどこに時間やチームのストレスがかかっているのか?を分析して最大の効果がある打ち手から実施していくと、運用が楽になり、チームの成果が上がりやすくなると思います。
もし自動化した後に一度もメンテしていないジョブがあれば、一度見なおしてみてはどうでしょうか。
Capistranoのデプロイの高速化を検討されている方は、一度 Recap を読んでみることをオススメします。
アカツキの開発環境ではテストとデプロイを別系列のジョブにしていますが、「テストが通った場合のみデプロイする」という方法を採用されている方は、クックパッドさんの RRRspec 等で高速化することも重要ですね。